Complex Analysis: #2 Analytic Functions
Any non-empty connected open set G ⊂ ℂ will be called a region.
(Recall that in ℜ2, every open connected subset is also path-connected.) So we will generally be interested in functions f : G → ℂ defined in regions.
Definition 2
Let f : G → ℂ be given, and let z0 ∈ G. If
exists, then it is the derivative of f at z0. The function f will be called analytic in G if it is defined, and has a continuous derivative everywhere in G. The word holomorphic is also used, and it is synonymous with the word analytic.
As in real analysis, we have the simple rules for combining the derivatives of two functions f and g:
Nevertheless, there is a very big difference between the idea of a derivative in complex analysis, and the familiar derivative in real analysis. The reason for this is that a common limit must exist, regardless of the direction with which we approach the point z0 in the complex plane. This leads to the Cauchy-Riemann differential equations.
Looking at the definition of the complex derivative, one immediately sees that it is really a special version of the total derivative (as in analysis 2) in ℜ2. Thus, for ξ ∈ ℂ sufficiently small (that is |ξ| small), we have
f(z0
+ ξ) = f(z0) + Aξ + |ξ|ψ(ξ),
where A is a 2 ×2 real matrix, and limξ→0 ψ(ξ) = 0. But what is A? It represents multiplication with the complex number f '(z0) = a + ib, say. That is,
So what are these real numbers a and b? Let f(z) = u(z) + iv(z), where u, v : G → ℜ are real functions. Then writing z = x + iy, we have f(x + iy) = u(x + iy) + iv(x + iy). Identifying ℂ with ℜ2, we can consider the partial derivatives of u and v. Since A is simply the Jacobi matrix of the mapping f at the point z0, we must have
These are the Cauchy-Riemann equations. Another way to express this is to simply say that we must have
Thinking in geometrical terms, we see that if f is analytic, then it is a conformal mapping, at least at the points where f ' is not zero. That means that, locally, the mapping preserves angles. Looked at up close, the mapping is
Of course, as we have already seen, the rotation preserves orientation. Thus it is an element of the group SL2 (R).
Another interesting detail is that the real and imaginary parts of an analytic function are themselves harmonic functions. Anticipating a later conclusion, let us assume that the parts of the analytic function f = u + iv are twice continuously differentiable. Since ∂u/∂x = ∂v/∂y and ∂u/∂y = −∂v/∂x, we have
Or, expressed in another standard form of notation,
uxx + uyy
= ∆u = 0.
Here, ∆ is the Laplace operator. Similarly, we see that ∆v = 0.
All of this shows that we cannot simply choose any old smooth function f : G → ℂ and expect it to be analytic. On the contrary, there is a very great “rigidity”, which means that most smooth functions — even though they may be partially differentiable when considered as mappings of 2-dimensional Euclidean space — are not complex differentiable.
Examples
- The first example is the nice and smooth function f(z) = f(x + iy) = x2 + y2. Here ux = 2x and vy = 0. But according to the Cauchy-Riemann equations, we must have ux = vy; that is, x = 0. This only holds along a single line in the complex plane ℂ. Therefore it certainly can’t hold in any region of ℂ (since regions are defined to be open), and thus f, despite all appearances of being a nice function, is definitely not analytic.
- Having been cautioned by the previous example, let us try to construct an analytic function. For example, let us assume that u(x + iy) = x. What possibilities are there for v(x + iy)? Since ux = 1 = vy and vy = 0 = vx, it is clear that the only possibility is v(x + iy) = y + constant. So this is just the rather boring function f(z) = z + constant.
- Thinking more positively, we have just seen that the simplest non-trivial polynomial, namely f(z) = z, is analytic throughout ℂ. Of course the simplest polynomial, f(z) = constant, is also analytic. But then, noting that we can use the sum and product rules for differentiation in complex analysis, we see that any arbitrary complex polynomial is analytic throughout ℂ. Indeed, z−n is also analytic (in ℂ \ {0}) for any n ∈ ℕ.




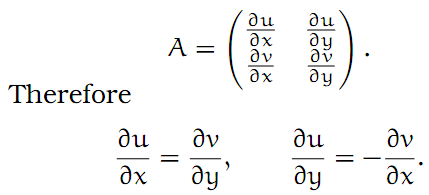



No comments:
Post a Comment
If it's a past exam question, do not include links to the paper. Only the reference.
Comments will only be published after moderation