Question 3 [Transition
Metals]
In
an isolated transition metal atom the five d orbitals have the same energy.
When a transition metal ion forms a tetrahedral complex the d orbitals are
split into two groups of different energies.
Reference: Past Exam Paper – 9701 March 2016 Paper 42 Q3
Solution:
a)
[electron configuration in Transition
Metals]
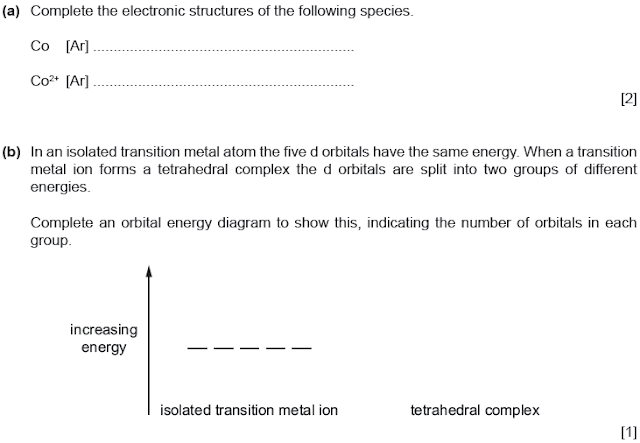
Co
[Ar] 4s2 3d7 Co2+
[Ar] 3d7
(recall,
in formation of a cation, electrons are first lost from 4s subshell than 3d.
This is due to 4s subshell being at a lower and more accessible energy level)
b)
[coloured compounds in Transition
Metals]
Splitting happens in ratio of 3:2 :: higher energy level: lower energy level.
(this
was a trick question, most commonly octahedral shapes are asked; in octahedral
complexes, 2 orbitals are promoted to a higher energy level while 3 remain on
lower level. It is the other way around for tetrahedral complexes.)
c)
i) [transitional metal complexes in Transition
Metals]
[Co(H2O)3(Cl)3]-
Few points to keep in mind:
-
Even though question states chloride
ions, we place no charge on the individual ligand- in both the diagram and
formula. Therefore [Co(H2O)3(Cl-)3]- is incorrect.
-
Calculation for overall charge must
always be done, it is NOT always the charge on the transition metal ion. Question states Cobalt(II) therefore net
charge= +2+3(0)+3(-1)= -1 [water is
a neutral ligand, chloride ions carry unit negative charge]
ii) [isomerism in Transition Metals]
When there are 2 different types of ligands, 3
each, the isomers are a special case of “fac-mer” isomerism.
Isomer
1 is a FAC isomer. With respect to water ligands, the plane created
(highlighted in pink) does NOT pass through the central metal ion. In case of
isomer 2(MER isomer), the plane created contains the central metal ions. These
are the only 2 possible isomers. All other versions will be identical to either
of these and will be penalised in the marking scheme.
d)i)
[Pt(NH3)2(Cl)2] [transitional metal complexes in Transition
Metals]
- Pt has charge +2 as stated in the
question
- NH3 molecules are neutral
ligands; charge=0
- Chloride ions carry -1 charge each.
- Therefore net charge= +2+2(-1)=0
Please
keep in mind, lone pair in NH3 is located on N atom, Therefore bonding must be
between N atom and Pt atom. Inversion of formula is necessary when ligand is
attached on left hand side(as seen in diagram 2)
iii)
Cis-platin; It is able to bind to (the guanine bases) in DNA strands
and this prevent DNA replication.
(this
is a memory based question. Trans-platin is ineffective in the body.)
e)
i) [stability constants in Transition Metals]
points
to note:
-
Brackets are very important
especially when dealing with complexes in Kstab
-
Sometimes double square brackets are
required ( as seen in the image); The inner square bracket is part of the
formulaic representation while the outer square bracket is the standard
notation for “concentration”.
-
Remember to write the net charge of
the complex after the first inner bracket.
-
Any stoichiometric coefficient in the
equation is transposed to become the power/exponent of its corresponding
species.
Solutions provided by Kashish Varshney, India








No comments:
Post a Comment
If it's a past exam question, do not include links to the paper. Only the reference.
Comments will only be published after moderation